Hello, this is Jooyoung Kim, an engineer and music producer.
Today, I will continue discussing the types of EQ from the previous post, focusing on Parametric EQ, Dynamic EQ, and Baxandall EQ.
5) Parametric EQ
Parametric EQ was designed by the renowned engineer George Massenburg. It is commonly found as a built-in EQ in DAWs.
This type of EQ allows you to select the frequency you want to adjust and set the Q Factor, which determines the bandwidth of the adjustment.
Parametric EQ is used not only for musical purposes but also for addressing issues with sound sources. It can handle problems such as proximity effect from microphones, Singer’s Formant (a specific resonance found in vocalists), room resonance, and high-pitched squeaking noises from strings.
6) Dynamic EQ
Dynamic EQ combines the functions of a compressor with an EQ. It works similarly to a multiband compressor but with slight differences in how bands are set and how it operates.
- A multiband compressor uses cut filters to define bands, while a Dynamic EQ defines bands according to the EQ settings.
As mentioned in the previous post, cut filters cause a phase shift of π/2 for every 6dB/oct. This means that multiband compressors can alter the sound due to phase changes even without any settings.
- Depending on the Dynamic EQ, most do not allow you to set the ratio, attack, and decay like a compressor does. Typically, you can only set the threshold and the amount of volume reduction or increase.
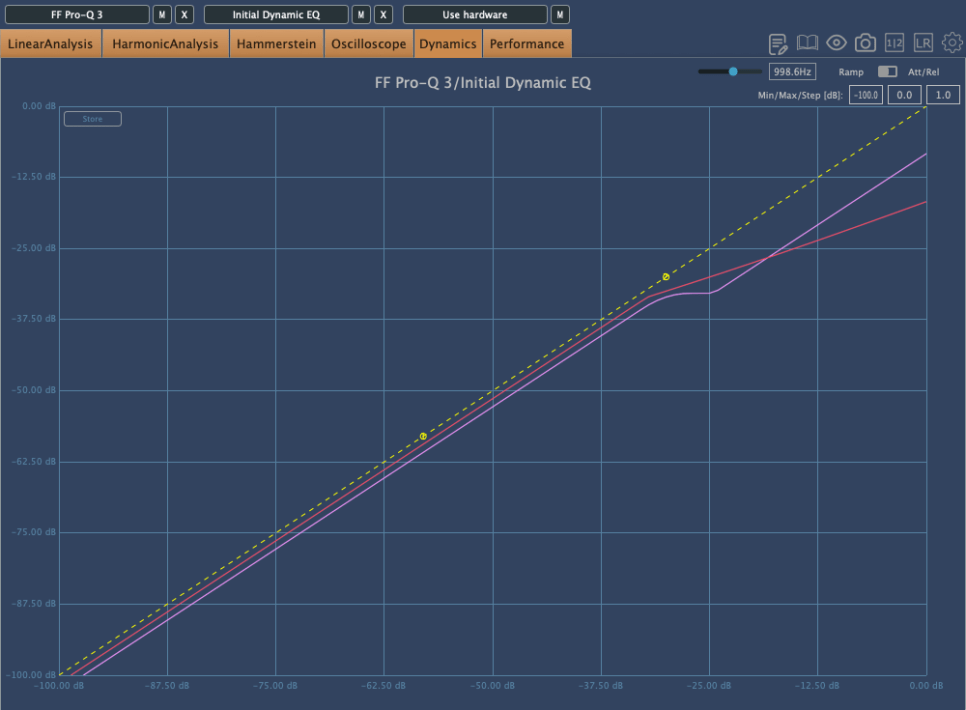
Because of this, the compression curve of a Dynamic EQ can appear different. The pink curve is from Fabfilter’s Pro-Q3, and the red curve is from Initial Audio’s Dynamic EQ. Although both are Dynamic EQs, their behavior is quite different.
Interpreting Fabfilter’s unique curve, it seems to compress the sound up to a certain point, after which it stops compressing and simply reduces the volume of the sound.
In simpler terms, for Pro-Q3, if the sound exceeds a certain level, it follows the dynamic curve (green) rather than the set yellow curve, acting more like a simple EQ.
However, their usage is generally similar. Dynamic EQs are often used when you want to reduce specific frequency bands. You can choose based on your preference.
7) Baxandall EQ

Baxandall EQ was introduced by Mr. Baxandall in 1952 through Wireless World magazine without royalties, making it widely used.
Due to its minimal phase issues, it is frequently used in mastering. It’s effective for adjusting broad frequency ranges, such as lifting high or low frequencies.
Examples include Tilt EQ and Dangerous’s Bax EQ.
This concludes the overview of various types of EQ. Besides these functional classifications, there are also categories like Zero Latency/Linear Phase/Normal EQs, and whether they are used for musical (Tone Shaping) or technical (Surgical) purposes.
I will continue with these topics in the next post.
See you next time!
