Hey there! I’m Jooyoung Kim, a mixing engineer and music producer.
Today, I want to talk about something light but super useful: how to properly export audio files after mixing and mastering.
Let’s dive in!
The Basics of Exporting Audio Files
Once mixing and mastering are complete, you typically need to export your tracks in multiple formats—WAV, FLAC, and MP3—to send to clients or distributors.
But here’s the catch: not all DAWs make this process easy. For example:
- Pro Tools and Logic Pro X don’t have built-in options to export FLAC files.
- Cubase supports FLAC, but you have to export each format individually, which can be a hassle.
I’ve previously written about audio codecs in my blog series Basics of Mixing.
To recap:
- WAV: The original, uncompressed file format.
- FLAC: A lossless compressed format.
- MP3: A lossy compressed format.
Both FLAC and MP3 use codecs that are freely available for encoding and decoding. So, why not use a simple script to automate the process?
Automating FLAC and MP3 Exports with Python
Here’s a quick and easy way to convert your WAV files to FLAC and MP3 using Python and the ffmpeg-python library.
Step 1: Install ffmpeg-python
First, make sure you have Python installed. Then, open your terminal (Mac) or command prompt (Windows) and run:
pip install ffmpeg-python
This might take a minute or two, but it’s worth it!
Step 2: The Python Code
Here’s a simple script to convert a WAV file to both MP3 and FLAC:
import ffmpeg
# 📂 Input file path
input_path = '/path/to/input.wav'
# 📂 Output file paths
output_mp3 = '/path/to/output.mp3'
output_flac = '/path/to/output.flac'
# ✅ WAV → MP3 (CBR - Constant Bitrate 320kbps; you can change '320k' to '256k' for different bitrates)
ffmpeg.input(input_path).output(output_mp3, audio_bitrate='320k', format='mp3').run()
# ✅ WAV → FLAC (compression_level: 0-8; higher numbers mean higher compression)
ffmpeg.input(input_path).output(output_flac, format='flac', compression_level='8').run()
Step 3: Save and Run the Script
- Copy the code above into a text editor.
- Mac users: Ensure your text editor is set to plain text (not RTF).
- Save the file with a .py extension (like convert_audio.py).
- Run the script using Python (like python convert_audio.py).
Voilà! You’ll have your FLAC and MP3 files in no time.
How to Find File Paths
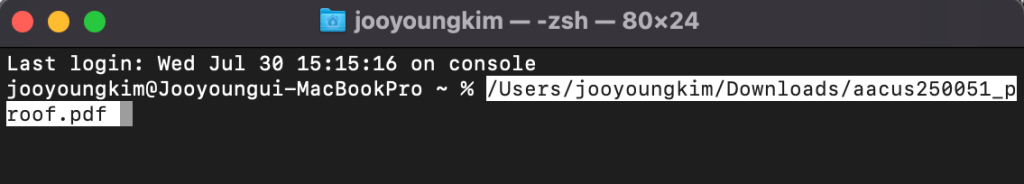
- Mac: Drag and drop your WAV file into the Terminal, and the file path will appear automatically.
- Windows: Right-click the file, select “Properties,” and copy the file path from there (you may need to adjust the path format slightly, use backslashes \).
Why This Matters
Manually exporting files in different formats can be a time sink, especially for long projects like live recordings over an hour. Using this script, you can:
- Save hours of repetitive work.
- Quickly generate high-quality FLAC and MP3 files.
A Few Notes
- Bit Depth and Sample Rate: For MP3 files, it’s standard to use 44.1kHz and 16-bit WAV files as the source. FLAC can handle higher resolutions (e.g., 48kHz, 24-bit) if needed.
- Dithering: FFmpeg’s dithering options are basic, so for WAV files with specific bit depth or sample rate conversions (e.g., 48kHz/24-bit to 44.1kHz/16-bit), it’s better to handle those in your DAW for better quality.
- MP3 Standards: Always use a 44.1kHz, 16-bit WAV file as the source for MP3 conversion to meet industry standards.
Final Thoughts
This is a super basic tip, but I couldn’t find many clear guides on this topic online, so I wanted to share it with you. If you’ve never coded before, this might seem intimidating at first, but trust me—it’s straightforward and will save you tons of time.
Give it a try, and let me know how it goes! Until next time, happy mixing! 🙂