Hey there! I’m Jooyoung Kim, a mixing engineer and music producer.
Looking at synthesizer history, additive synthesis came first but was limited to physical, mechanical methods. Modern additive synthesis came much later, so let’s start with subtractive synthesis!
Quick heads-up: if you buy virtual instruments through the links in this series, I get a small commission, which really helps me keep going. ^^ Ready to dive in?

Subtractive synthesis is named for how it shapes sound by filtering out (subtracting) frequencies. The “filter” here is like an EQ’s cutoff filter, tweaking low or high frequencies.
These synths use voltage to control filters, hence the term VCF (Voltage Controlled Filter). Built entirely with analog circuits, they’re also called analog synthesizers.
They have three main parts:
- VCO (Voltage Controlled Oscillator): Generates the signal
- VCF (Voltage Controlled Filter): Shapes the sound
- VCA (Voltage Controlled Amplifier): Controls volume
The Iconic Minimoog Model D

The Moog Minimoog Model D is the most famous subtractive synth, with others like the ARP 2600, Oberheim OB-1, and Korg MS-20 also standing out. Let’s check out the Minimoog Model D virtual instrument, a favorite for many.
UAD’s Moog Minimoog
Since most subtractive synths share similar concepts, we’ll use the UAD Minimoog as our example. It breaks down into four sections:
- VCO: Oscillators (signal generators)
- VCF: Filters with resonance control
- VCA: Amplifiers with Attack, Decay, Sustain controls
- Modulation and other components
Let’s look at the oscillators first.
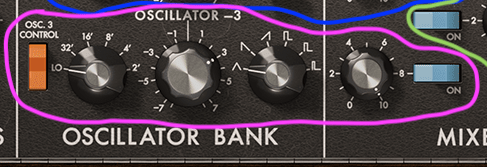
Oscillators
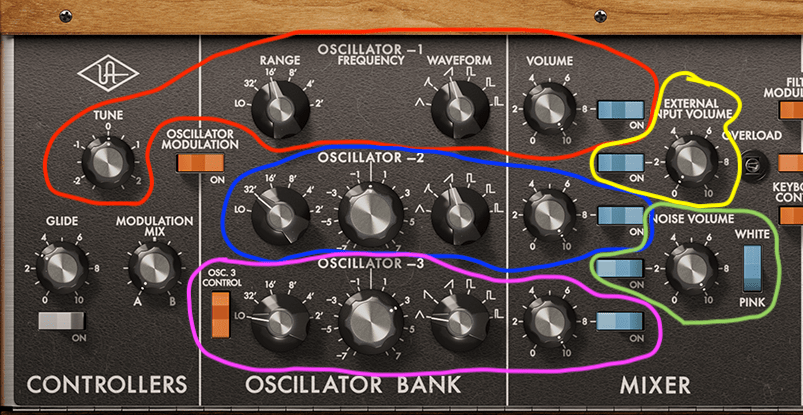
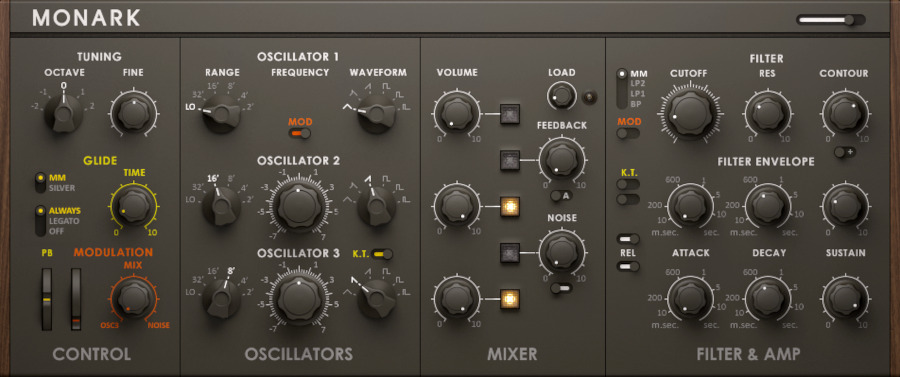
The oscillator section has about five parts. Oscillators 1, 2, and 3 are exactly what they sound like—three separate oscillators.
Being fully analog, the Minimoog Model D’s tuning could drift due to humidity, temperature, runtime, or electrical conditions. So, each oscillator has a pitch tuning knob. The tuner’s at the far left in the red section (labeled “Tune”), with others in the blue and pink sections.
- Range: Sets the octave. Higher numbers give lower pitches.
- Waveform: Chooses the waveform type.
Oscillator 3 could be used for modulation instead of sound output, controlled by a switch on the far left.
The yellow section, though not an oscillator, lets you process external signals through the synth’s filter—a feature often used to apply the Minimoog’s filter to other sounds.
The green section is a noise generator for white or pink noise. You can modulate with noise, an extra LFO, or an envelope filter.
Filters and Output
The filter section is the top three knobs in the “Modifiers” area:
- Cutoff Frequency: Sets which frequencies to filter.
- Emphasis: Boosts frequencies near the cutoff point.
- Amount of Contour: Controls how much the Attack, Decay, and Sustain knobs affect the filter.
Below, the Loudness Contour (Attack, Decay, Sustain) shapes the output sound’s envelope, not the filter’s. (I explained Attack, Decay, and Sustain in my last post.)
Turn on the Filter Modulation switch, and the cutoff frequency gets modulated. The Keyboard Control switches make the cutoff follow keyboard notes:
- Switch 1 (top): Tracks by 1/3.
- Switch 2 (bottom): Tracks by 2/3.
- Both on: Cutoff moves in sync with notes for consistent timbre.
It might feel tricky, but tweak it for five minutes, and you’ll get the hang of it.
Other Minimoog Model D Virtual Instruments
Besides UAD’s Minimoog, there are other solid options:

Arturia’s Mini V is a great Model D emulation.
Air Music Technology also makes a Model D virtual instrument.
As mentioned, the Minimoog can filter external signals. There are even standalone filter plugins, like:

Arturia’s Filter Mini, a plugin designed for this purpose.
Not all Moogerfooger pedals from Moog come from the Minimoog, but the Moogerfooger MF-101 Lowpass Filter uses its 4-pole (24dB/octave) ladder filter design. Moog turned these pedals into plugins too.
I’ve covered these separately before. [link]
Owning a Physical Model D

I always wanted a real Minimoog Model D and ended up with Behringer’s Model D reissue. Hardware synths shine when run through preamps or compressors for a fully analog vibe. But tuning is a chore, and since it’s monophonic, you’d need to record each note for chords. Also, dusting those knobs is a nightmare! 😅
Still, it’s affordable, so a used analog synth like this can be a cool addition.
Not all subtractive synthesis synthesizers work exactly like the Minimoog, but understanding its basics should give you a solid foundation for handling most early subtractive synths.
See you in the next post! 🙂