Hello! This is mixing engineer and music producer Jooyoung Kim.
Last week, while I was writing my paper, I discovered logical structure and measurement errors. As a result, I had to export data several times and couldn’t post anything on the blog. However, the first article at 2025 is Basics of Mixing! This article is based on “Basics of Mixing“, published in South Korea.
Today, we’ll find out types of analog cable and connectors. Let’s dive in!
Types of Cables

Cables can be divided into two categories: Analog & Digital.
Analog:
1) Balanced
2) Unbalanced
Digital:
1) AES/EBU(AES3)
2) ADAT
3) S/PDIF
4) MADI
5) LAN(UltraNET, CobraNet, Dante..etc)
In this article, I’ll talk about analog cables and connectors.
Analog Balanced Cable & Unbalanced Cable
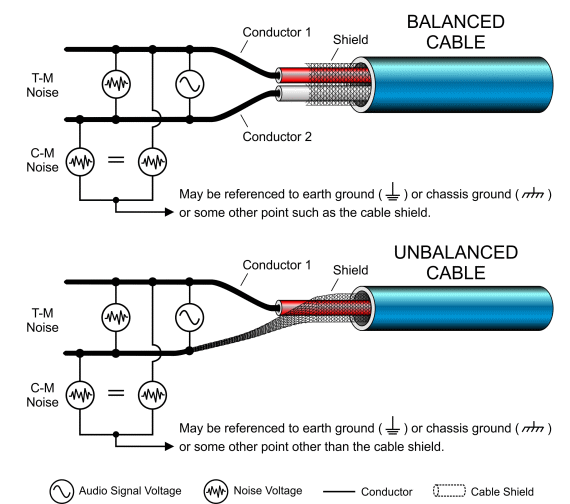
First, you have to know difference between balanced cable and unbalanced cable.
Generally balanced cable has 3 lines: Hot(+), Cold(-), Ground. The hot and cold lines carry identical signals but in opposite phases, which helps cancel out noise.
Unbalanced has 2 lines: Hot(+), Ground.
You can convert a balanced cable into an unbalanced stereo cable by assigning the hot and cold lines to the left and right channels, respectively.
Analog Connectors

Representable connector, for balanced cables, are TRS and XLR. You could see 3 parts for hot, cold, and ground.
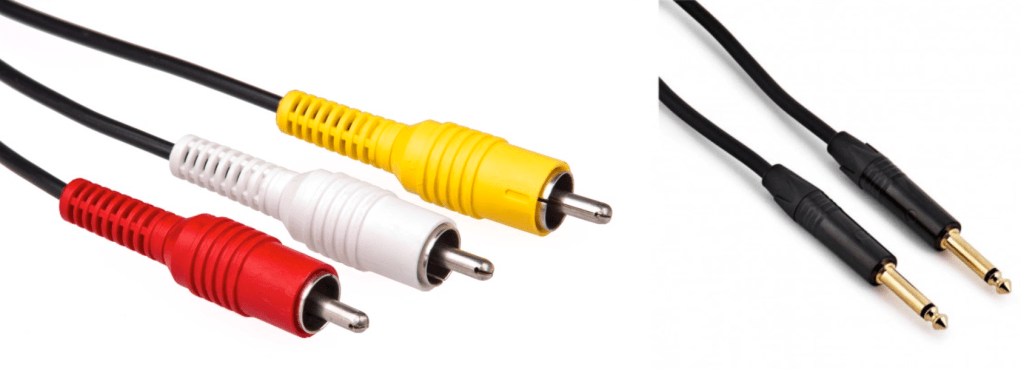
RCA and TS cable is the most used connector for unbalanced cable

Common consumers easily find this AUX connectors at headphones or earphones.

Banana and SpeakON connectors are also used at unbalanced cable, for passive speakers.
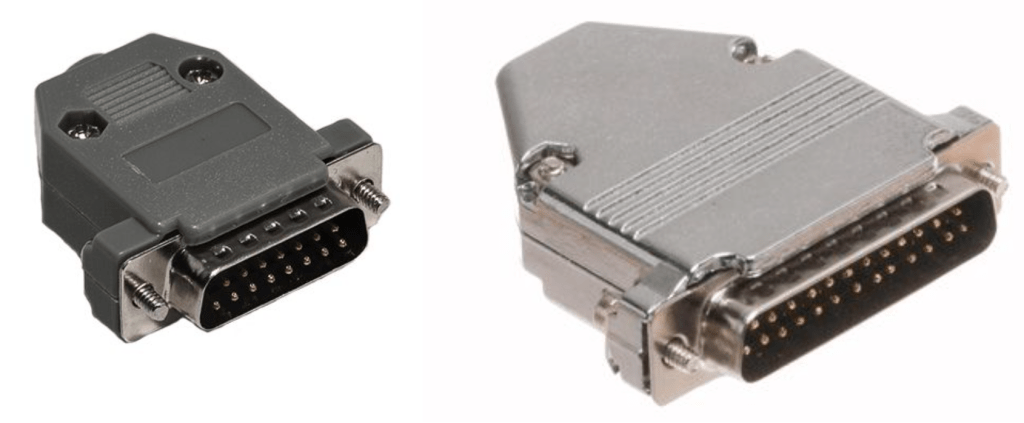
If you purchase audio interface, sometimes you could find those connectors. Those connectors called D-Subs. DB25 connectors could connect analog balanced 8 channels. DB15 connectors are not used usually.

There is also a proprietary patchbay-specific standard called TT cable.
These guys are so small and expensive, so unless you’re working with an analog mixer, I think it’s better to just buy a TRS patch bay and use TRS.
Well, in fact, if it’s copper, you can use it as an analog cable. You can cut the power cable that you don’t use at home and use it as a balanced cable. I haven’t tried it, but you can probably cut the USB cable and use it.

There is no disagreement about digital, but there is a lot of talk about the difference in sound quality depending on the type of analog cable and connector. This depends greatly on the specific situation.
Guitarists will feel the difference in cables quite a bit when performing or playing together, but this is mostly due to the high impedance of the electric guitar and the impedance of the amplifier. When recording directly connected to a proper DI box or audio interface, you won’t be able to feel the difference. So, to compare properly, you should record by micing the connection to the amplifier.
For the same reason, you may feel it a little in the cable connected to the microphone preamp and the microphone.
However, it is actually meaningless for cables at line level. If you are connecting speakers or outboard, you don’t have to think about this. I also bought a slightly expensive Telefunken STMC cable and used it on the microphone, and… I thought… haha..
I should have bought several pizzas or hamburgers with that money.

If you are an engineer, you will probably end up soldering it yourself because you don’t want to waste any extra wires or connectors. If you look inside, you will see that it is a very simple structure. Don’t hesitate to try it yourself—you’ll find that it’s simpler than it looks!
I will end it here for today. Then, I will see you again in the next article!